It’s crazy season, that special time on the American calendar when aspiring candidates for the nation’s highest office try to outdo each other in an effort to attract more voters to their platforms. This time around, background support is provided by a virtual anvil chorus of anti-capitalism clatter. Senator Elizabeth Warren, for example, frequently unleashes criticism of American capitalism by asserting that the “system is rigged,” a complaint that seems to resonate with meaningful populist appeal. It’s an old refrain that has echoed across the years from Karl Marx onward.
Nobel Laureate Robert J. Shiller explains why this may be the case in his new book, “Narrative Economics.” As Shiller points out, when a story is repeated enough, the viral message may be accepted as conventional wisdom, more like an article of belief than a matter of reason.
I’ll also emphasize that for a message to prevail, it helps if its content rests on a preexisting and inherently moral foundation that reflects our tribal instincts as an evolved human species. And what works for a small tribe doesn’t necessarily work so well for a huge industrialized nation.
Consider this: Some may inquire, “Do you believe in capitalism?” almost as if the position one takes is a matter of religion. When answering, we reflect on our tribal preferences, and cooperating and sharing with our family and neighbors is often a key to success. Thus, many people will almost instinctively answer “no,” or at least “yes, but …” followed by some serious caveats and exceptions.
Yes, the beneficial-but-invisible hand of commerce driven by self-interest has never been an instinctually lovable idea. Gains from trade, while well-documented since the days of Adam Smith, can be more elusive than we may first realize. Given the widespread negative views on the subject, politicians’ calls for greater accountability and government intervention may not be welcomed by all, but they’re understandable.
Shiller adds another dimension to his narrative economics story by using data from Google’s Ngram Viewer. The viewer produces charts based on the frequency of particular words and phrases in Google Books, which include some 8 million downloaded volumes in various languages.
Consider an Ngram we might apply to Senator Warren’s comments. The nearby figure contains one for “system is rigged” that shows the frequency of the phrase’s occurrence from 1940 through 2008, the final year in the database. I have smoothed the data by using a three-year running average:
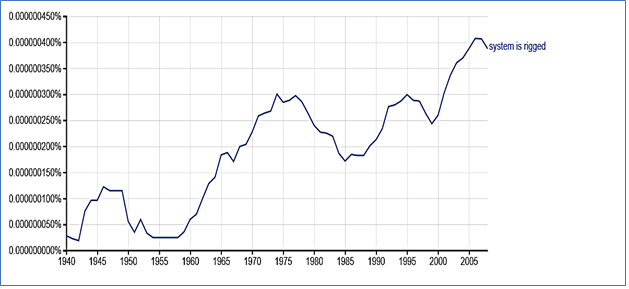 The data show four viral periods: 1940-1950, 1960-1985, 1990-1998, and 2000-2008. The first period encompasses World War II, a time of draft, rationing, price controls, defense contracting, and related cronyism that may in some cases have been highly profitable for hand-picked firms.The second viral period is much longer and encompasses a period including the Vietnam War and related draft, Watergate and significant social unrest.The third period includes the first Iraq war, and the fourth contains anti-capitalism protests and budding expressions of concern about income inequality as a version of the economy closer to what we know today took shape.The Ngram suggests that in seeking to communicate to her base, Senator Warren artfully chose a phrase that had gone viral before—which is to suggest that there may be an embedded tribal norm that reacts during periods when a relatively small number of people are able to build large fortunes or avoid burdens, such as the draft, as a result of government actions and favors.Oddly enough, Senator Warren and other capitalism critics seldom ask how the system got rigged and what might be done to undo the rigging. But of course, the rigging is done in Washington, sometimes when special interest groups—including corporations—lobby congress for favorable treatment.
The data show four viral periods: 1940-1950, 1960-1985, 1990-1998, and 2000-2008. The first period encompasses World War II, a time of draft, rationing, price controls, defense contracting, and related cronyism that may in some cases have been highly profitable for hand-picked firms.The second viral period is much longer and encompasses a period including the Vietnam War and related draft, Watergate and significant social unrest.The third period includes the first Iraq war, and the fourth contains anti-capitalism protests and budding expressions of concern about income inequality as a version of the economy closer to what we know today took shape.The Ngram suggests that in seeking to communicate to her base, Senator Warren artfully chose a phrase that had gone viral before—which is to suggest that there may be an embedded tribal norm that reacts during periods when a relatively small number of people are able to build large fortunes or avoid burdens, such as the draft, as a result of government actions and favors.Oddly enough, Senator Warren and other capitalism critics seldom ask how the system got rigged and what might be done to undo the rigging. But of course, the rigging is done in Washington, sometimes when special interest groups—including corporations—lobby congress for favorable treatment.
And how might that be undone? By trimming away uneven regulation and adopting policies that expose all business firms to the refreshing winds of competition. Put another way, by forcing capitalists to act like capitalists and not lobbyists.













